
Vehicles to communicate with other vehicles, infrastructure, and the internet
To protect computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, theft, damage, or disruption.
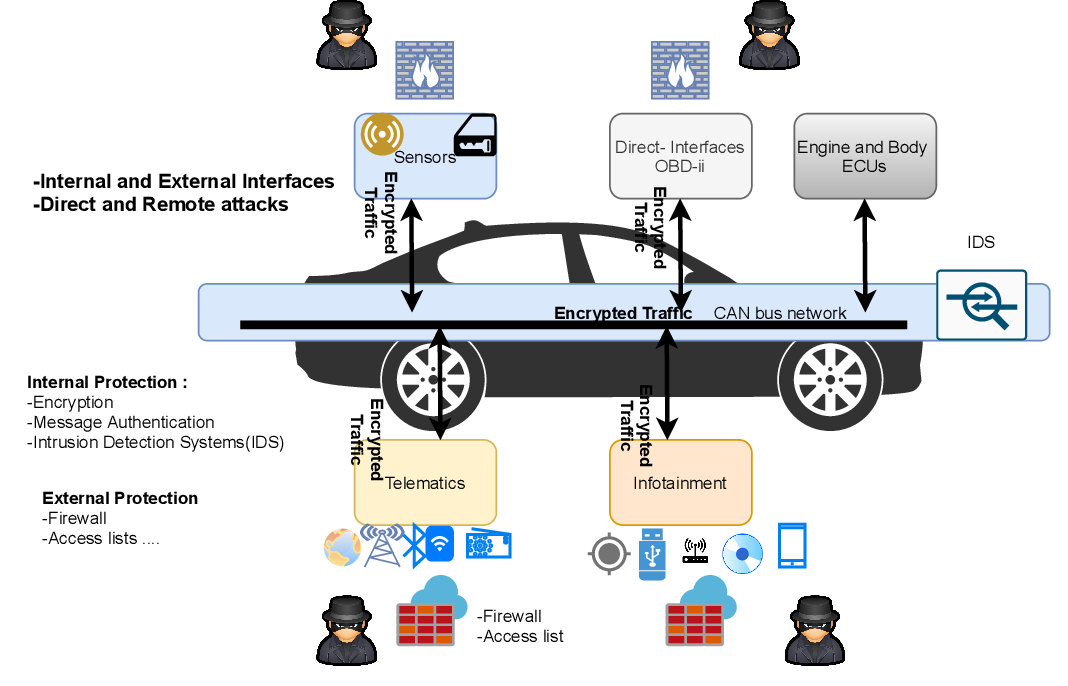
Introduction: As vehicles become more connected and technologically advanced, the need to prioritize automotive cyber security has never been greater. The integration of software systems, network connectivity, and advanced features in modern vehicles introduces new vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals. we delve into the realm of automotive cyber security, exploring the challenges, solutions, and best practices to ensure the safety and integrity of vehicles in an increasingly digital landscape.